DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.623237
One-Liner (thrice)
- Used features extracted by VGGish from raw acoustic audio against a SVM, Perceptron, 1NN; got \(59.1\%\) classif. accuracy for dementia
- Then, trained a CNN on raw wave-forms and got \(63.6\%\) accuracy
- Then, they fine-tuned a VGGish on the raw wave-forms and didn’t report their results and just said “we discovered that audio transfer learning with a pretrained VGGish feature extractor performs better” Gah!
Novelty
Threw the kitchen sink to process only raw acoustic input, most of it missed; wanted 0 human involvement. It seems like last method is promising.
Notable Methods
fine-tuning VGGish against raw acoustic waveforms to build a classifier via a CNN.
Key Figs
Their fancy network
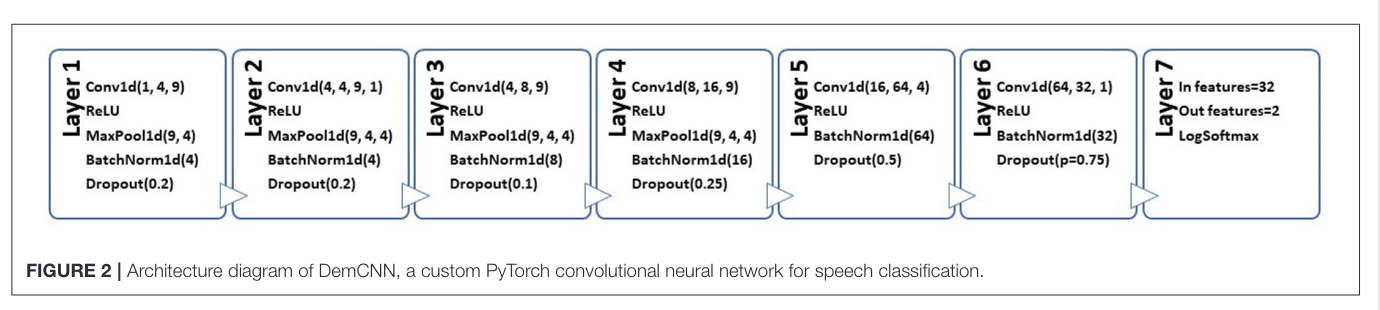
Its just a CNN afaik with much maxpooling; could have used some skipped connections. I wonder if it overfit?
Their actual training results
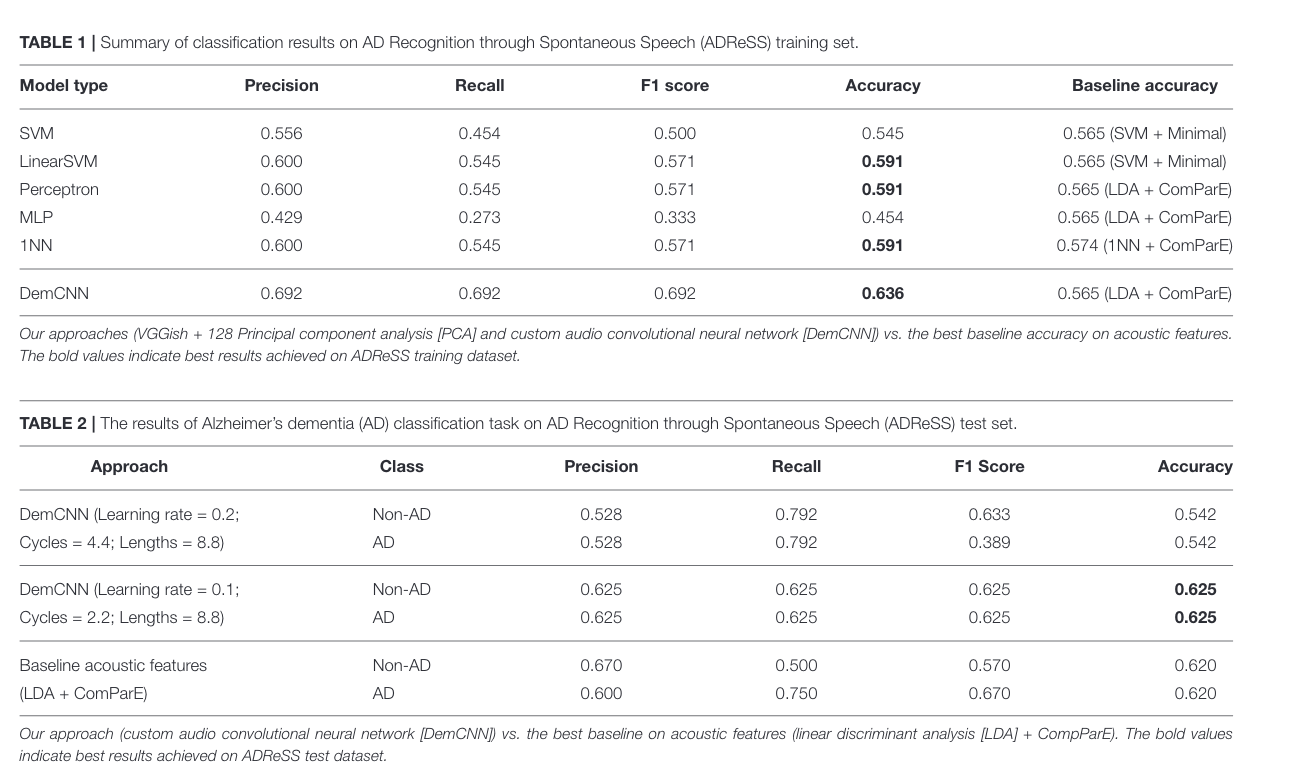
Looks generally pretty bad, but a run of their DemCNN seem to have gotten state-of-the-art results. Not sure where transfer training data went.
New Concepts
Notes
Accuracy question
According to this the state of the art at the time from pure audio was 56.6%? For a binary classifier isn’t that just doing nothing?

So somebody did get better before?