#Ntj
Parvin 2020
Last edited: June 6, 2022DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2020.605317
One-Liner
An excercize scheme has had some measured effect on theta/alpha ratio and Brain wave frequency on AD patients; prognosis of AD not controlled for.
Novelty
- Leveraged physical training scheme and measured EEG effects by quantifying theta/alpha ratio
Notable Methods
- Used theta/alpha ratio as assay for improvement, and found the exercise scheme did so p<0.05
- Only tested patients with AD w/o a control for stage
Key Figs
Figure 1
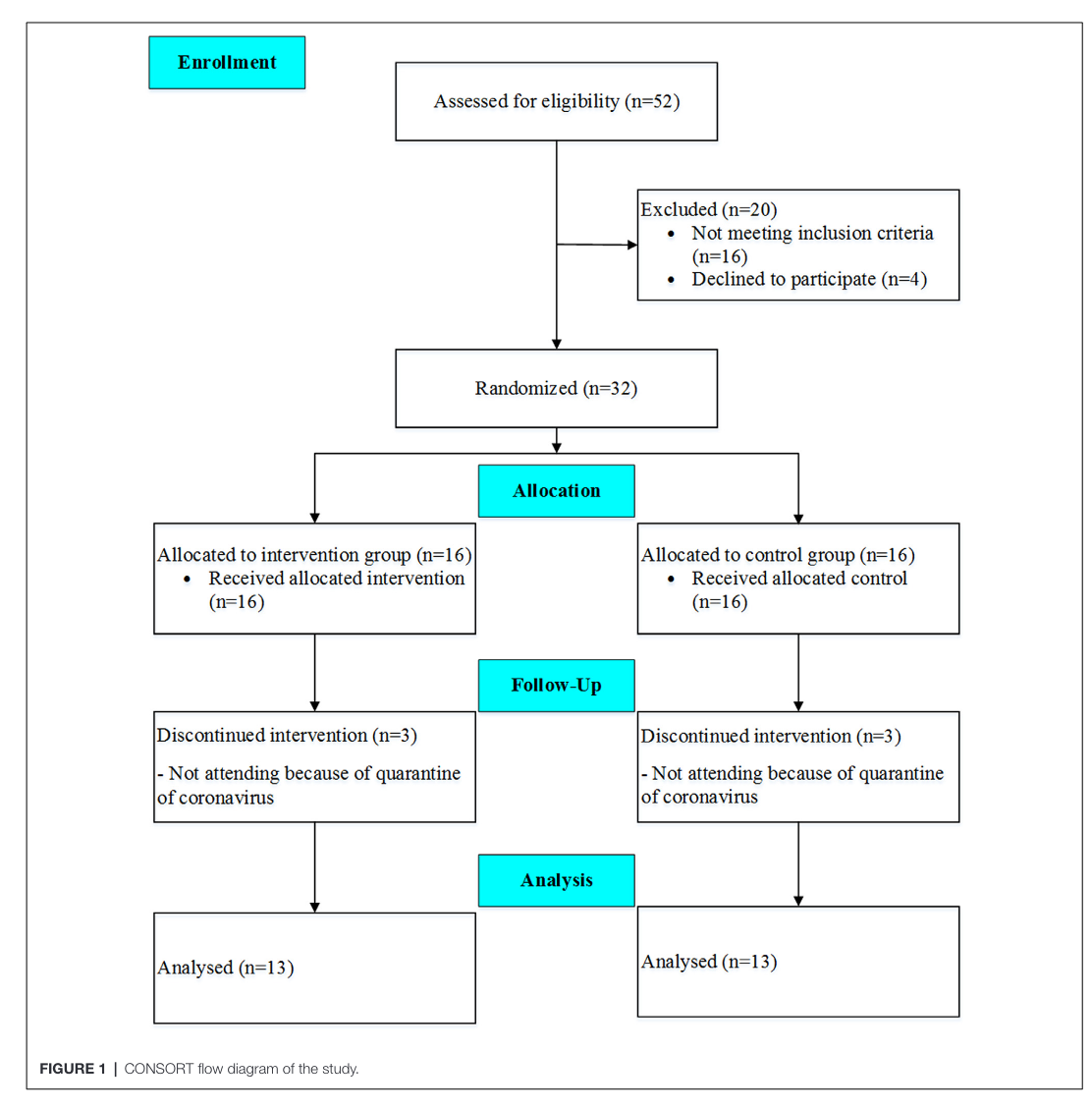
This figure tells us th N number of participants through the study
Zhu 2021
Last edited: June 6, 2022DOI: 10.3389/fcomp.2021.624683
One-Liner
late fusion of multimodal signal on the CTP task using transformers, mobilnet, yamnet, and mockingjay
Novelty
- Similar to Martinc 2021 and Shah 2021 but actually used the the current Neural-Network state of the art
- Used late fusion again after the base model training
- Proposed that inconsistency in the diagnoses of MMSE scores could be a great contributing factor to multi-task learning performance hindrance
Notable Methods
- Proposed base model for transfer learning from text based on MobileNet (image), YAMNet (audio), Mockingjay (speech) and BERT (text)
- Data all sourced from recording/transcribing/recognizing CTP task
Key Figs
Figure 3 and 4
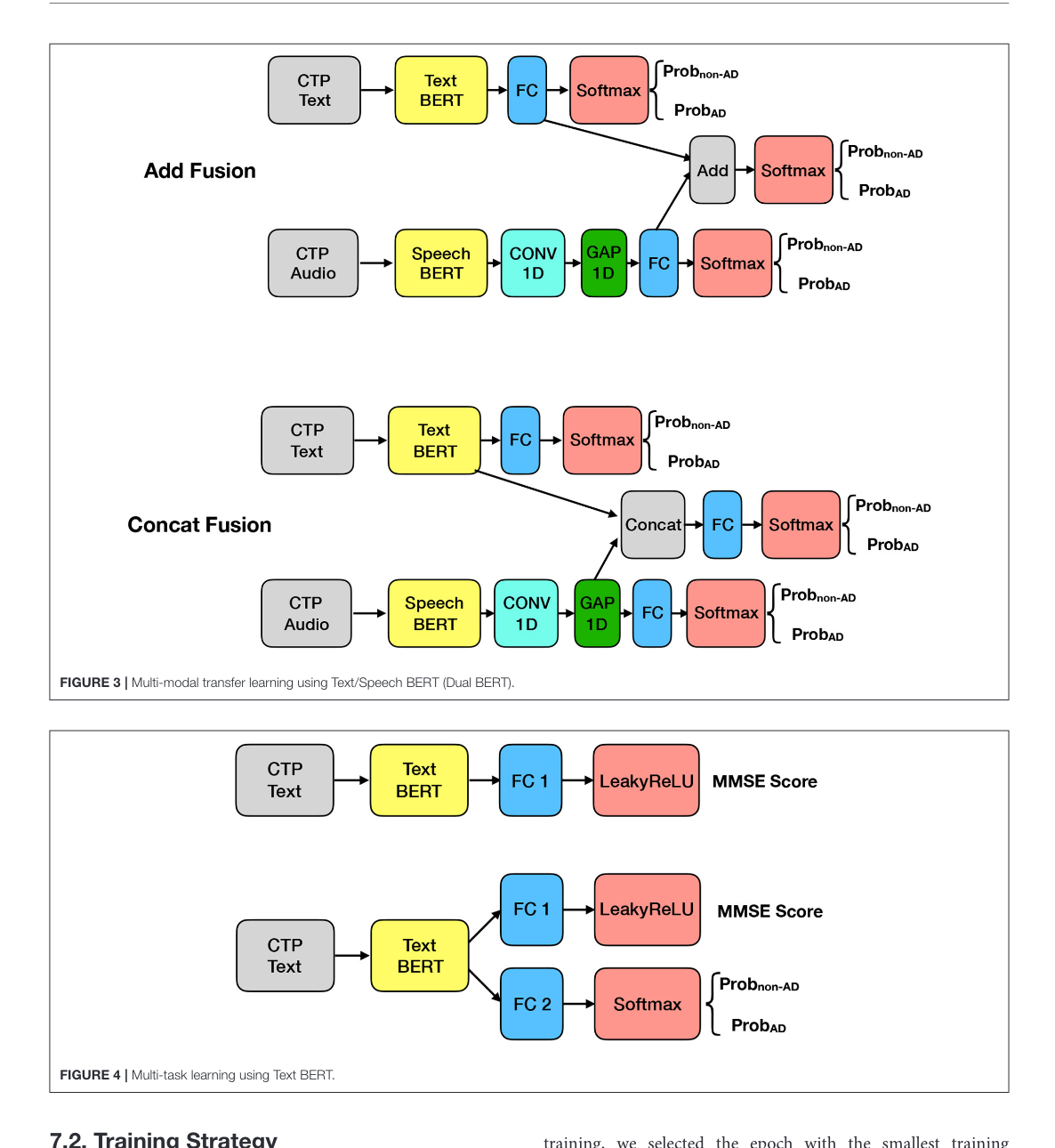
This figure tells us the late fusion architecture used
Lindsay 2021
Last edited: June 6, 2022DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.642033
One-Liner
Proposed cross-linguistic markers shared for AD patients between English and French; evaluated features found with standard ML.
Novelty
Multi-lingual, cross-linguistic analysis.
Notable Methods
Key Figs
Figure 1
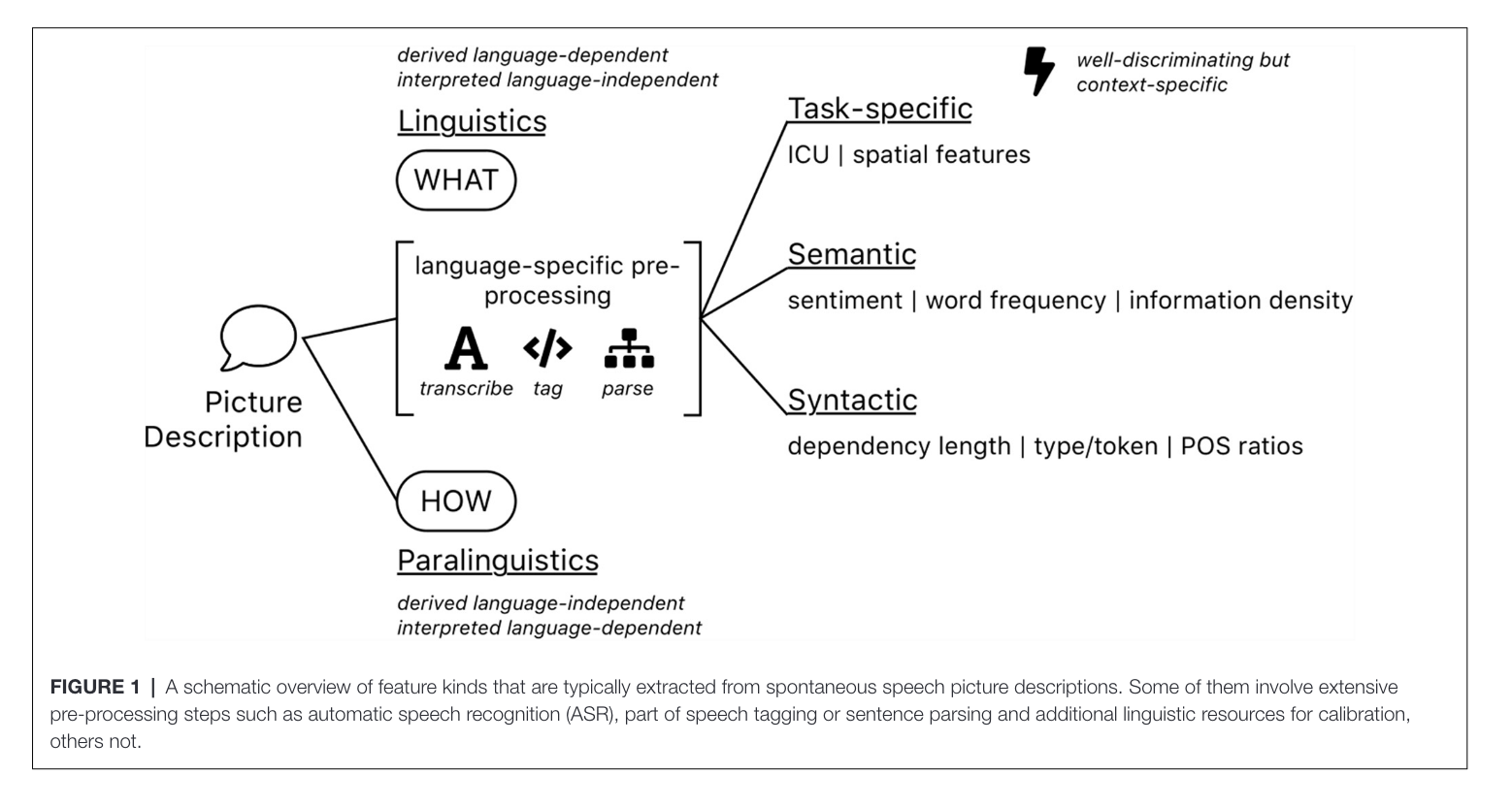
This figure tells us the various approaches measured.
Table 2
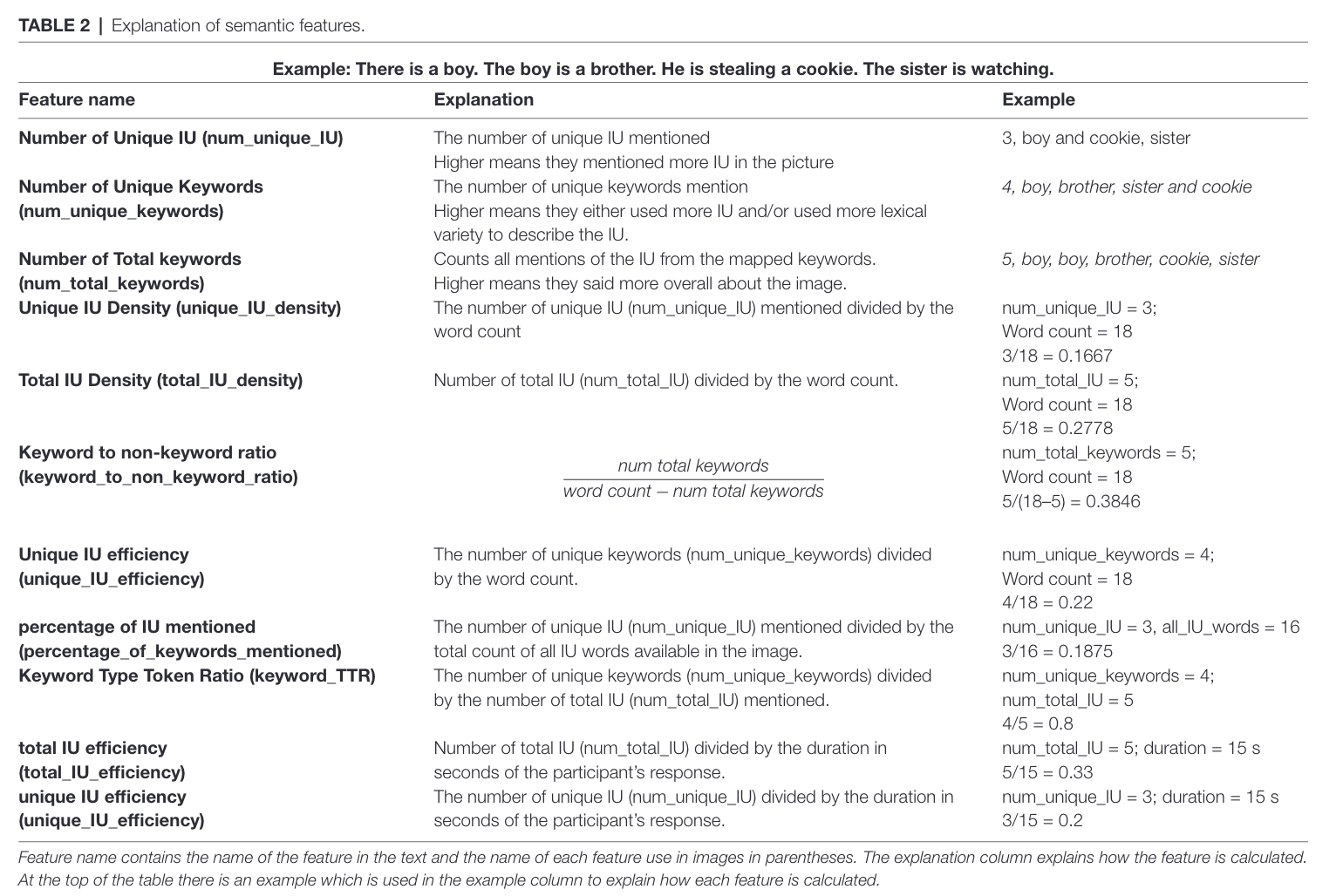
Here’s a list of semantic features extracted
Table 3
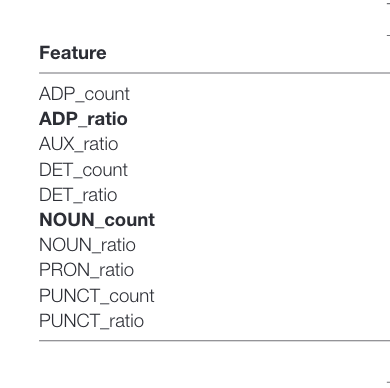
Here’s a list of NLP features extracted. Bolded items represent P <0.001 correlation for AD/NonAD difference between English and French.
Antonsson 2021
Last edited: June 6, 2022DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2020.607449
One-Liner
oral lexical retrieval works better than qualitative narrative analysis to classify dementia; and semantic fluency + Disfluency features chucked on an SVM returns pretty good results.
Novelty
Tried two different assays of measuring linguistic ability: oral lexical retrieval metrics, and qualitative discourse features analysis of speech.
Notable Methods
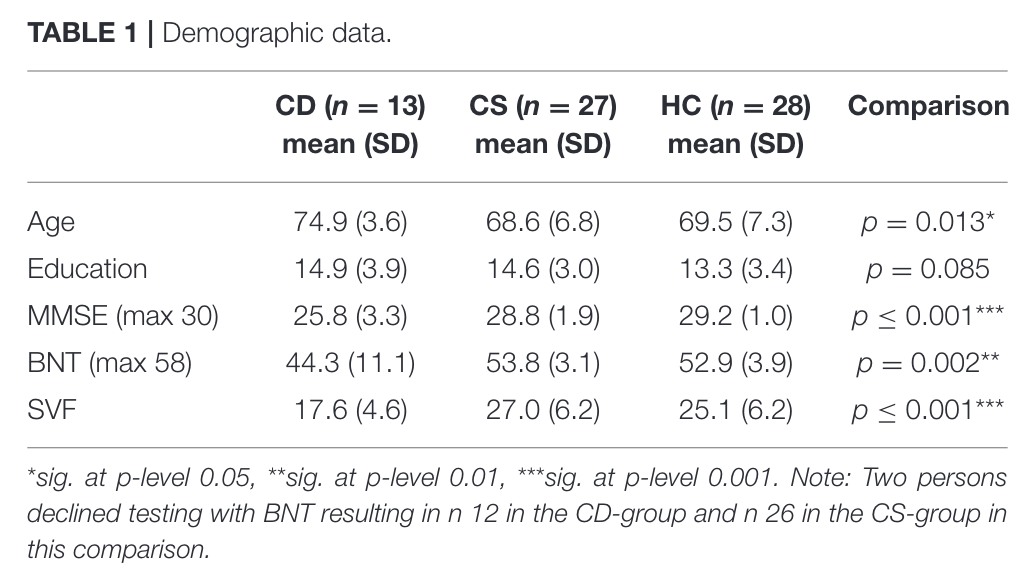
Subjects divided into three groups
- Great cog. decline
- Impaired but stable
- Healthy controls
Administered BNT and SVF tests as baseline
Key Figs
Table 3
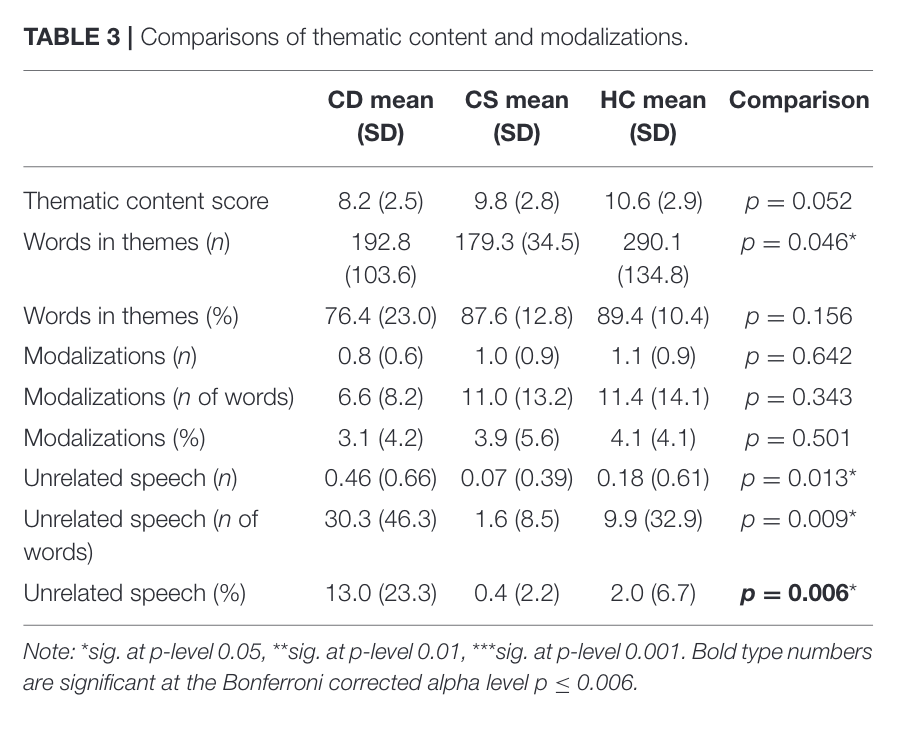
This figure tells us that the percentages of unrelated utterances was a statistically significant metric to figure differences between the three experimental groups.
Chlasta 2021
Last edited: June 6, 2022DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.623237
One-Liner (thrice)
- Used features extracted by VGGish from raw acoustic audio against a SVM, Perceptron, 1NN; got \(59.1\%\) classif. accuracy for dementia
- Then, trained a CNN on raw wave-forms and got \(63.6\%\) accuracy
- Then, they fine-tuned a VGGish on the raw wave-forms and didn’t report their results and just said “we discovered that audio transfer learning with a pretrained VGGish feature extractor performs better” Gah!
Novelty
Threw the kitchen sink to process only raw acoustic input, most of it missed; wanted 0 human involvement. It seems like last method is promising.