Meghanani 2021
Last edited: August 8, 2025DOI: 10.3389/fcomp.2021.624558
One-Liner
analyzed spontaneous speech transcripts (only!) from TD and AD patients with fastText and CNN; best was \(83.33\%\) acc.
Novelty
- threw the NLP kitchen sink to transcripts
- fastText
- CNN (with vary n-gram kernel 2,3,4,5 sizes)
Notable Methods
- embeddings seaded by GloVe
- fastText are much faster, but CNN won out
Key Figs
the qual results
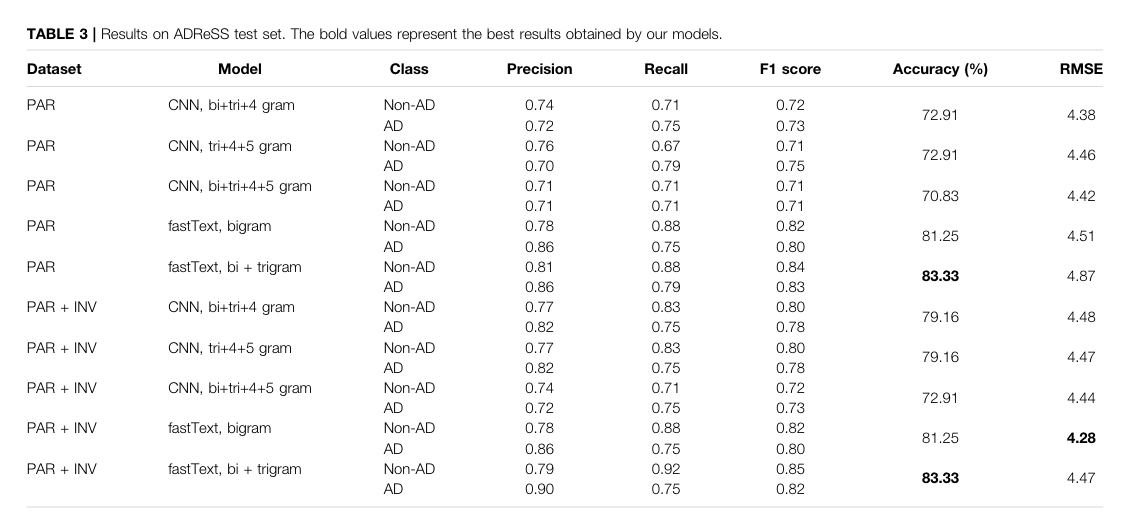
PAR (participant), INV (investigator)
Notes
Hey look a review of the field:
Parvin 2020
Last edited: August 8, 2025DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2020.605317
One-Liner
An excercize scheme has had some measured effect on theta/alpha ratio and Brain wave frequency on AD patients; prognosis of AD not controlled for.
Novelty
- Leveraged physical training scheme and measured EEG effects by quantifying theta/alpha ratio
Notable Methods
- Used theta/alpha ratio as assay for improvement, and found the exercise scheme did so p<0.05
- Only tested patients with AD w/o a control for stage
Key Figs
Figure 1
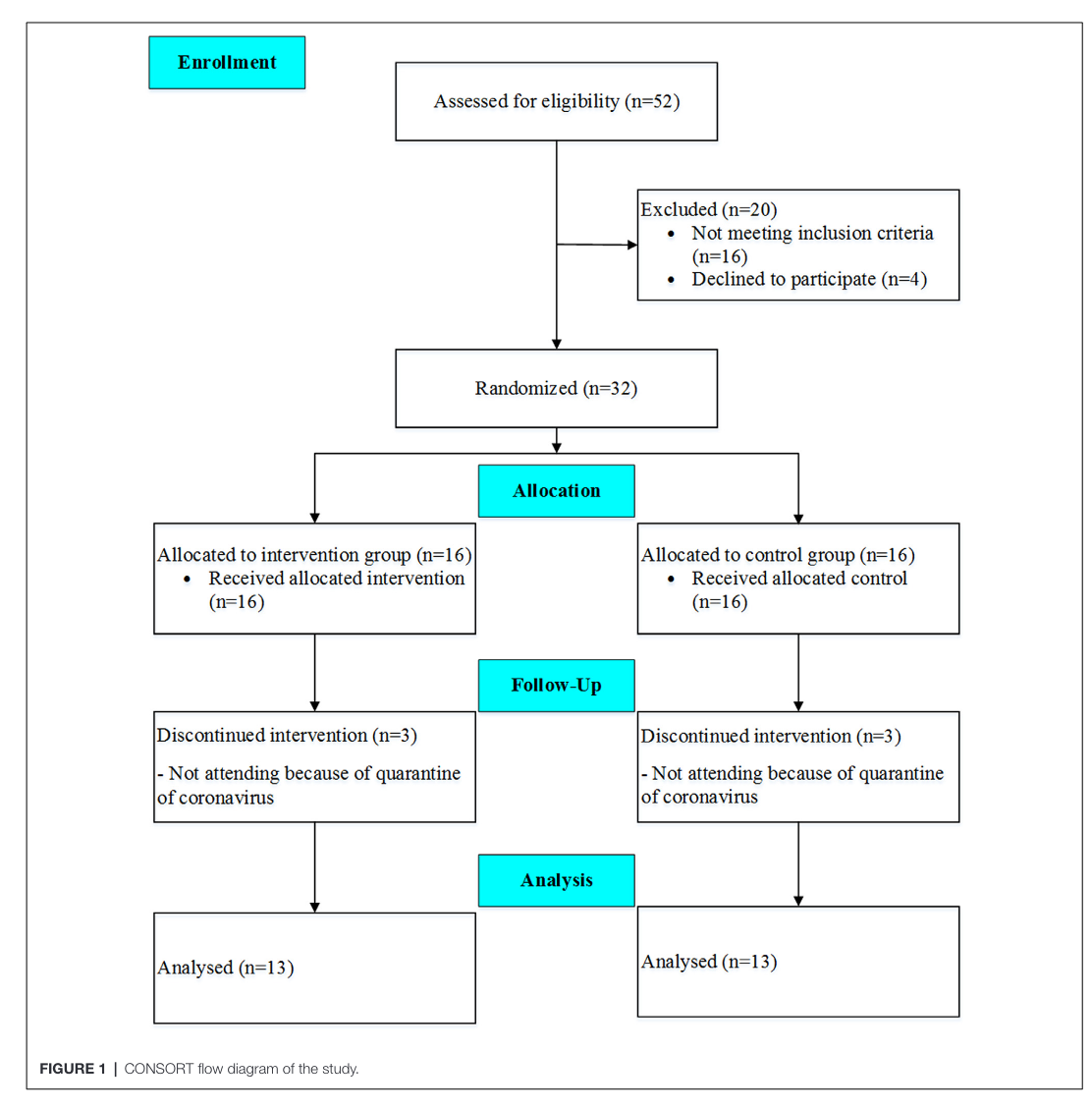
This figure tells us th N number of participants through the study
Sadeghian 2021
Last edited: August 8, 2025DOI: 10.3389/fcomp.2021.624594
(Sadeghian, Schaffer, and Zahorian 2021)
One-Liner
Using a genetic algorithm, picked features to optimize fore; achieved \(94\%\) with just MMSE data alone (ok like duh me too). Developed ASR tool to aid.
Novelty
- Developed an ASR methodology for speech, complete with punctuations
- Used a genetic algorithm to do feature selection; NNs performed worse because “space is smaller???”
Notable Methods
Used a GRU to insert punctuations
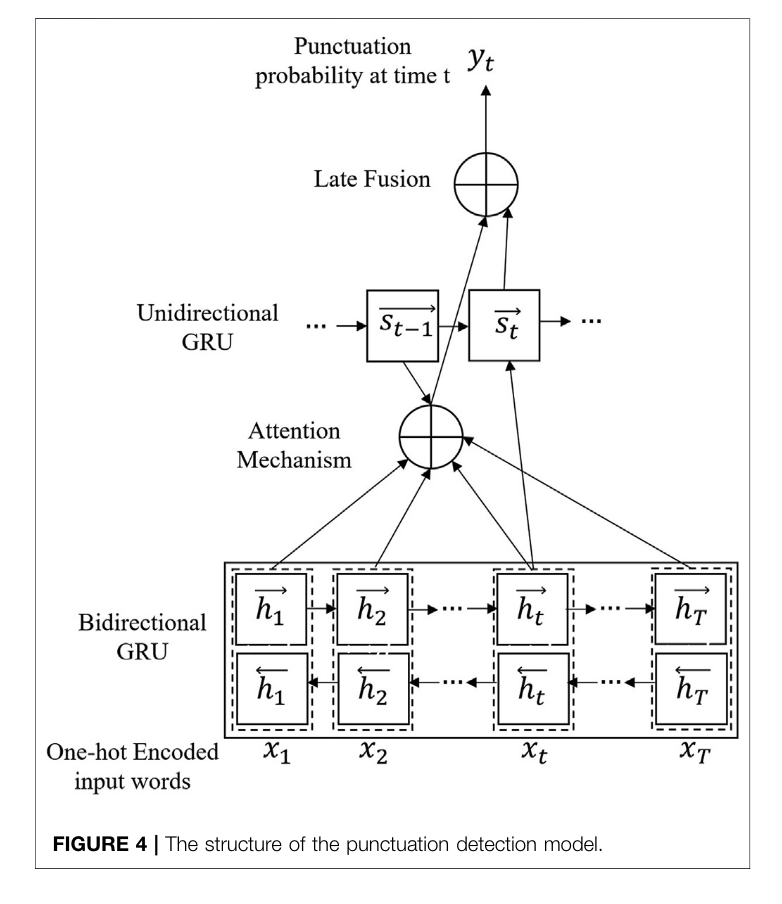
The paper leveraged the nuke that is a bidirectional GRU, ATTENTION,
Shah 2021
Last edited: August 8, 2025DOI: 10.3389/fcomp.2021.624659
One-Liner
Multi-feature late fusion of NLP results (by normalizing text and n-gram processing) with OpenSMILE embedding results.
Novelty
NLP transcript normalization (see methods) and OpenSMILE; otherwise similar to Martinc 2021. Same gist but different data-prep.
Notable Methods
- N-gram processed the input features
- Used WordNet to replace words with roots
Key Figs
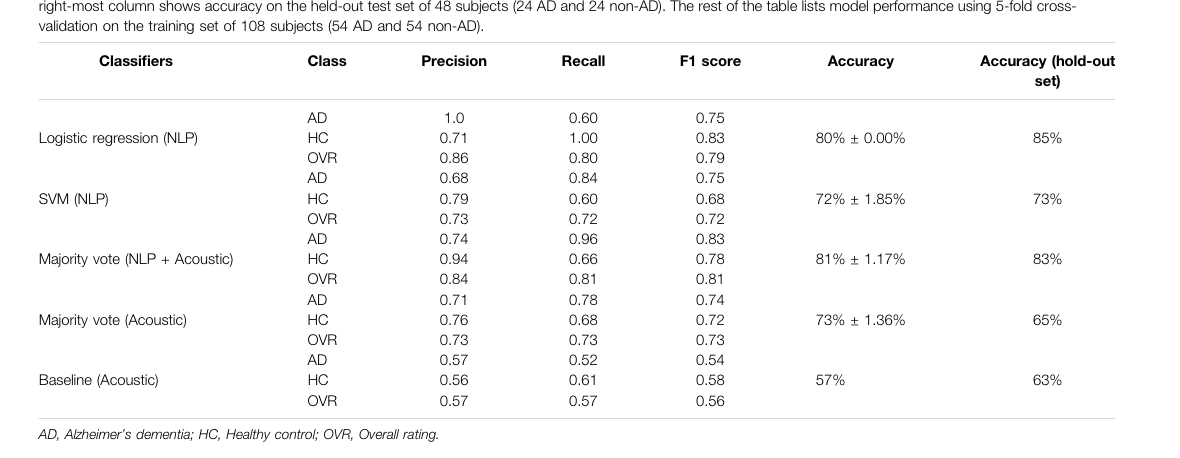
New Concepts
Yuan 2021
Last edited: August 8, 2025DOI: 10.3389/fcomp.2020.624488
One-Liner
Used an ERNIE trained on transcripts for classification; inclusion of pause encoding made results better.
Novelty
- Instead of just looking at actual speech content, look at pauses specific as a feature engineering task
- \(89.6\%\) on the ADReSS Challenge dataset
Notable Methods
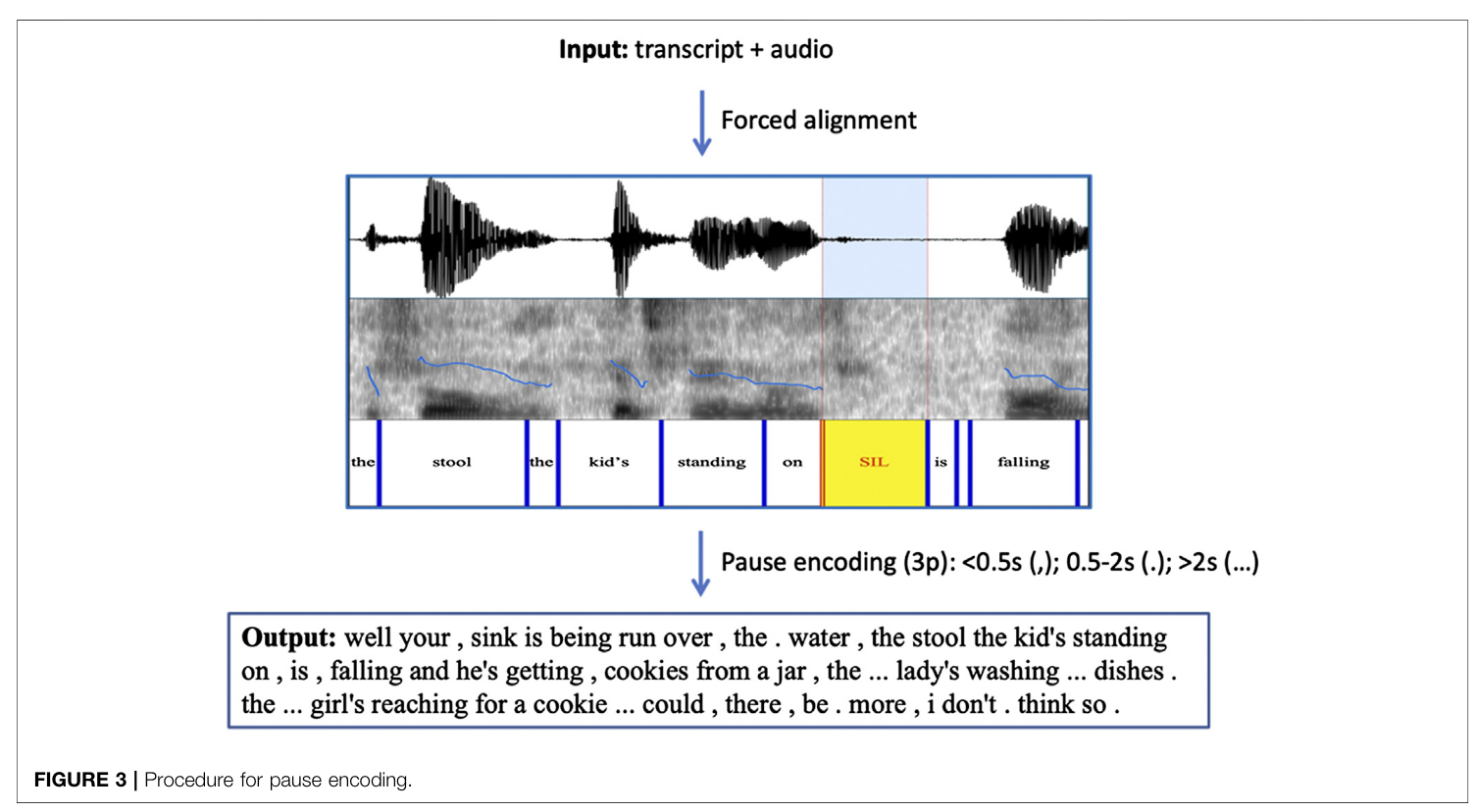
Applied FA with pause encoding with standard .cha semantics (short pauses, medium pauses, long pauses). Shoved all of this into an ERNIE.
Assay for performance was LOO